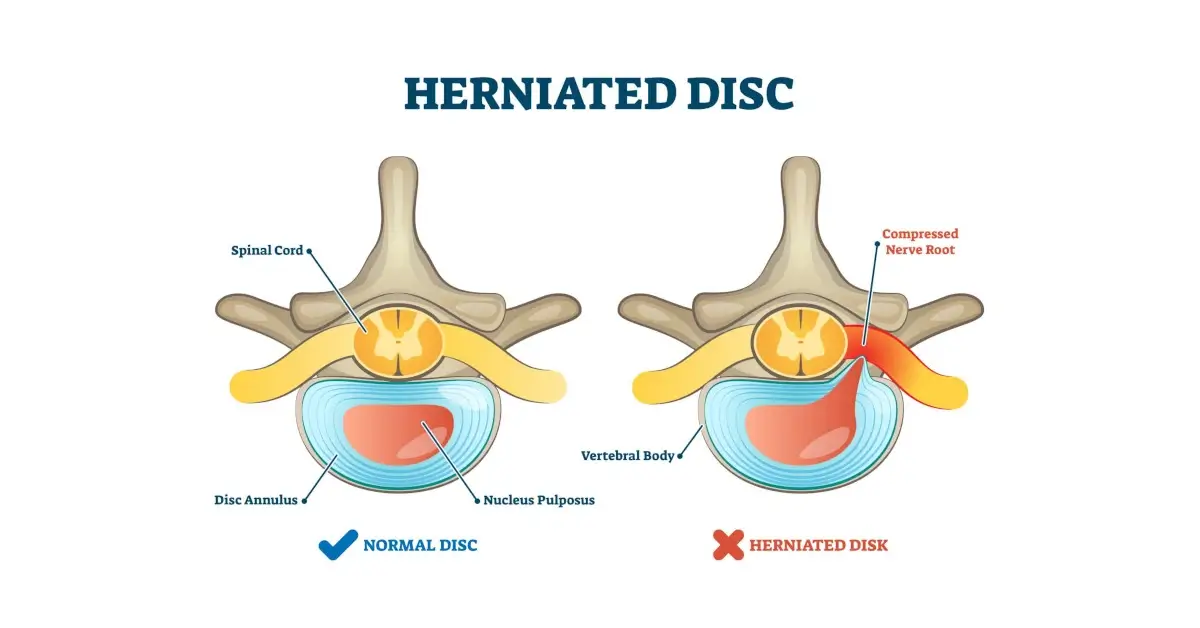
Also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, a herniated disc is a condition in which the soft center of a spinal disc leaks through the tough exterior and presses on nearby nerves or nerve roots. This results in sharp, acute pain that may radiate down the leg (depending on the location of the affected disc).
Disc herniation may occur due to degenerative disc disease or trauma from an incident, such as a fall, a motor vehicle accident or improper lifting of a heavy object.
Regarding the latter, there are ways to avoid developing a herniated disc in situations that involve lifting heavy objects (one of the most common causes of the condition). Here’s a list of those suggestions:
- Assess the situation: Does the object seem as if it’ll be too difficult to lift on your own? Would moving the object be easier with assistance?
- Know where to go: If you plan to lift and carry a large object by yourself, mentally plan out the route you’ll take to reach your destination. This will cut down on your lifting time and help you avoid tripping over obstructions. Discuss the plan with others, if you’re receiving lifting assistance.
- Bend your knees: This is a tried and true method for proper lifting that keeps your back from potential and unnecessary strain.
- Keep your back straight: While bending at the knee, straighten your back as if you were stuck to a rod. In this lifting position, your knees should be bent and your back and head should be upright to avoid the use of lower back muscles. In addition, avoid twisting or bending your body.
While these tips can prove helpful, many lifts, slips, falls and accidents are simply unavoidable. And when they result in a herniated disc, there are a variety of treatment options for disc herniation and their related symptoms.
Treatment Options for Disc Herniation
If you end up suffering from disc herniation, surgical and non-surgical treatments options are available for managing pain. Those options include medication, therapy and surgery.
Medications
Over-the-counter medications (OTC): For pain that is only mild to moderate, medications such as naproxen (e.g., Aleve©) and ibuprofen (e.g., Advil®) may offer relief.
Narcotics: Should OTC medications fail, your physician may prescribe narcotics for a small period of time.
Nerve pain medications: Though these medications are designed for nerve-damage pain, they may also be used in place of narcotics due to their milder side effects.
Muscle relaxers: Muscle relaxers are used to ease muscle spasms associated with disc herniation.
Injections: Guided by spinal imaging, corticosteroids may be injected into the area around the spinal nerve to reduce pain, swelling and inflammation.
Therapy
A physical therapist can recommend an exercise regimen to minimize pain from disc herniation as well as other treatment modalities, including:
- Electrical stimulation
- Heat and ice compressions
- Short-term neck and back bracing
- Traction
- Ultrasound therapy
Surgery
In the majority of cases, conservative methods of treatment are affective in relieving symptoms of a herniated disc. When these treatments fail, however, back surgery may be necessary to remove some of or the entire damaged disc. Should the entire disc be removed, the vertebrae will then be fused together with hardware to stabilize the spine.
The Center for Musculoskeletal Disorders of NY & NJ
If you are concerned that your back pain may be the result of a herniated disc, our non-surgical pain management specialists at the Center for Musculoskeletal Disorders of New York and New Jersey offer relief. Our practice offers comprehensive pain management services that are tailored to your individual needs.
For more information on disc herniation or to schedule an appointment with one of the orthopedic specialists, contact us today.